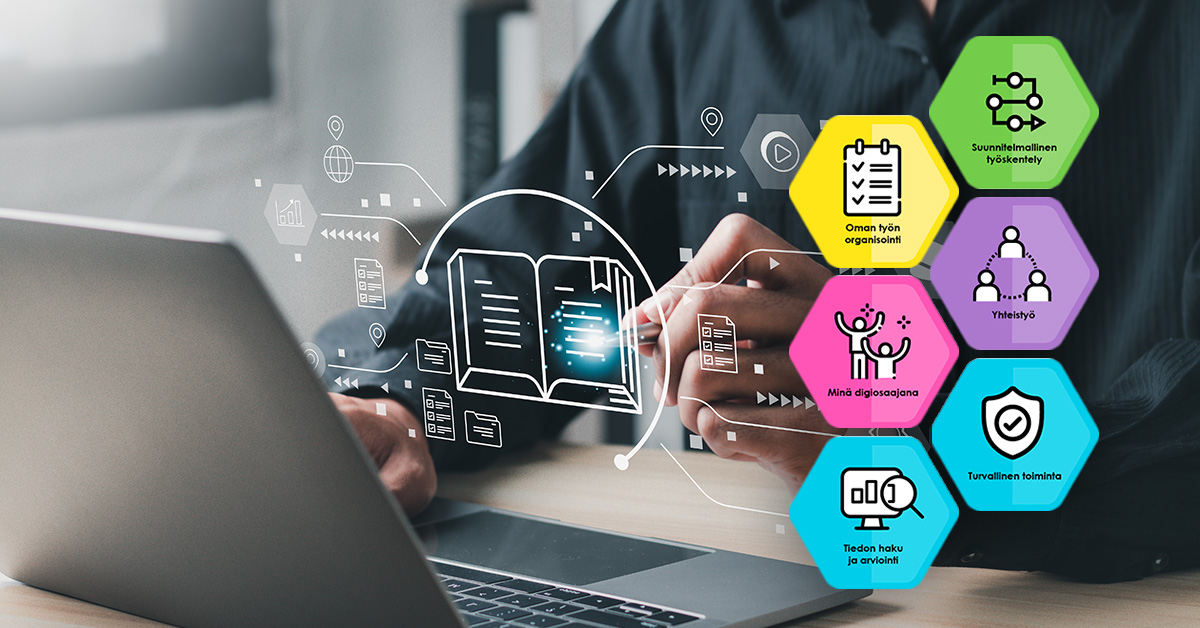
With the rapid pace of technological development, continuous learning and updating of skills are essential. The nationwide digital skills badge constellation maintained by TIEKE Finnish Information Society Development Centre is a practical means of identifying and articulating digital skills. The constellation helps individuals to plan their careers, and companies to identify their staff’s skills.
Technology is an important support for continuous learning and the identification of skills. One of the best practical examples of this is the national digital skills badge constellation maintained by TIEKE. Developed to meet rapidly changing skills needs, it is a ready-made model for identifying and articulating digital know-how.
Merja Sjöblom, Accelerator of Digital Skills at TIEKE, points out that digital skills badges can be used by educational institutions, teachers, businesses, or indeed anyone.
“Skills badges are useful for any individual, workplace or leisure organisation. The badges are tangible proof of a person’s digital skills, making them easy to identify and demonstrate.”
Useful for recruitment, career planning and more
Digital skills are divided into five levels: Basic Skills, Digital Skills, Collaborator, Utiliser, and Convergent Thinker. Under each of these levels there are different badges to obtain.
The skills badge constellation helps in career planning by showing the individual in practical terms what they need to learn. According to Sjöblom, companies that are recruiting also benefit from skills identification, as the applicant can clearly demonstrate their skills with the badges.
“There is no skill that cannot be identified. The identification of skills relates to leadership, language skills and skills acquired through volunteering, and more.”
Demonstration of skills
The competence of all ten badges is demonstrated with badge applications. Familiarize yourself with the contents and badges of each level: Basic skills, Digital skills, Collaborator, Utiliser and Convergent thinker.
-
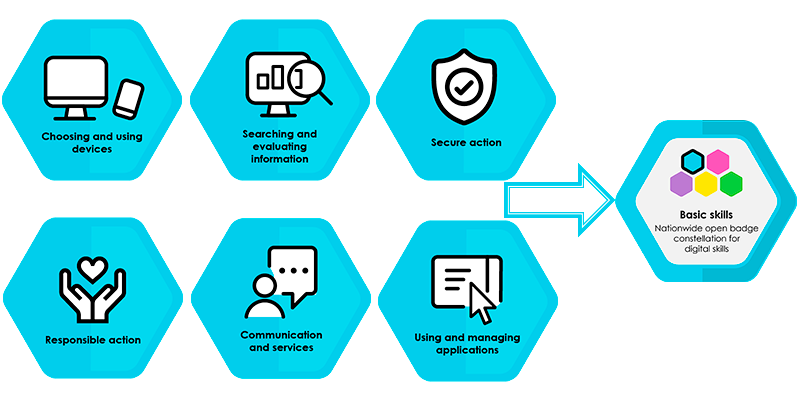
Basic Skills
Basic skills -level constains six badges. The milestone badge is earned after all six badges are granted.
Choosing and using devices: Recipient of the badge can
- identify and select the appropriate device (e.g., computer, tablet, telephone)
- use the most common digital devices and their basic functions and settings
- check whether they are connected to a wireless or wired network
Searching and evaluating information: Recipient of the badge can
- search for information in digital environments (keywords, search engines)
- search for information in different formats (text, image, video)
- evaluate the reliability of digital content
- recognise how copyright is related to information and information sharing
Secure action: Recipient of the badge can
- identify the most common cyber threats and information security threats
- protect their devices (e.g., antivirus software, device locking and blocking malware)
- recognise when their information security has been violated and act accordingly
Responsible action: Recipient of the badge can
- recognise how the use of digital devices and applications impacts health and well-being
- use messaging services and social media services in a responsible manner
- take copyright into account when using and sharing information
- create and edit digital image content (presentation graphics) in compliance with copyrights
Communication and services: Recipient of the badge can
- recognise their rights and responsibilities when disclosing their information to electronic services
- use electronic services
- recognise strong identification methods
- protect their personal information and privacy
- recognise and comply with the principles of data protection
- use email and its basic features
Using and managing applications: Recipient of the badge can
- select and use word processing and spreadsheet applications
- identify different file formats
- produce standard text documents
- make spreadsheets and use formulas to perform calculations
- process and transfer data in different formats
KUVA
Basic skills milestone badge
The recipient of the Basic skills milestone badge is able to use digital devices and services safely and in a responsible manner when communicating and using services. They are able to search for information in digital environments, assess the reliability of the information, and protect their personal information and privacy. They are able to use the most common office applications and use, produce and share digital content in compliance with copyrights.
-
Digital skills
Digital skills milestone badge is earned after Basic skills milestone badge and Digital me badge are issued.
The recipient of the Digital me badge can:
- manage and protect their own digital identity
- identify factors affecting their own digital footprint
- understand the difference between personal and professional presence in digital environments
- identify their own digital skills and development needs

The recipient of the Digital skills milestone badge is able to manage and protect their digital identity when acting personally or professionally in digital environments and social media. They identify development needs related to their digital competences.
-
Collaborator
Collaborator milestone badge is earned after Digital skills milestone badge and Collaboration badge are issued.
Recipient of the Collaboration badge can
- use digital tools to collaborate and produce
- edit, combine and develop digital content into a new format
- store, transfer and share digital content using digital tools
- utilize and select appropriate copyright licenses

The recipient of the Collaborator milestone badge is able to use digital tools to collaborate and produce, as well as to store and share information. They use, produce and distribute digital content. They are familiar with copyright and can choose the right copyright license for the intended purpose.
-
Utiliser
Utiliser milestone badge is earned after Collaborator milestone badge and Organizing you work badge are issued.
Recipient of the Organizing your work badge can
- use a variety of applications for organizing their work
- promote their own digital welfare by utilising good practices in knowledge work
- utilise self-management (self-regulation and time management) tools
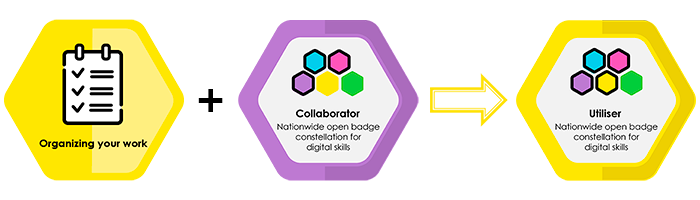
The recipient of the Utiliser milestone badge is able to use a variety of applications and tools to carry out and organise work and self-management. He/she knows good practices in knowledge work and is able to promote their own digital welfare.
-
Convergent thinker
Convergent thinker milestone badge is earned after Utiliser milestone badge and Problem solving and planning badge are issued.
Recipient of the Problem solving and planning badge can
- independently identify challenges in digital environments
- identify opportunities created by new technologies at work and in everyday life
- use digital technology in a versatile way to search for, review and generate new information
- solve problematic situations methodically and make justified proposals for development

The recipient of the Convergent thinker milestone badge has completed all ten Open Badges for digital skills. The recipient is a versatile digital expert who recognizes and can solve challenges when using digital devices and environments. The recipient uses digital technology independently and collaboratively to generate information and solve problems.
TIEKE helps in skills recognition
- The open badges are practical tools for skills recognition.
- The constellation benefits all parties: both individuals and various organisations and businesses.
- The open badges can be used in a number of ways. You can
- make use of existing constellations. The digital constellations are an easy way to confirm your own digital skills. Learn about the open-badge constellation of digital skills and start using them.
- develop new constellations with us for new areas. We are currently developing open badges in several projects.
- get help for developing open badges for your own organisation. For example, Helsinki Region Environmental Services HSY tailored their open badges for their own needs with TIEKE’s assistance (article in Finnish).
- increase understanding of open badges in a network. TIEKE coordinates the Badge Finland network and holds seminars to present various ways of making use of open badges. Learn about the network and future seminars (in Finnish).











